
29 May agrochemical : Boosting Agricultural Productivity and Sustainability
agrochemical play a vital role in modern agriculture, enabling farmers to maximize crop yield, combat pests and diseases, and promote sustainable farming practices. This comprehensive guide will delve into the world of agrochemicals, highlighting their significance, types, responsible usage, and their contribution to agricultural productivity and environmental stewardship.
Understanding Agrochemicals
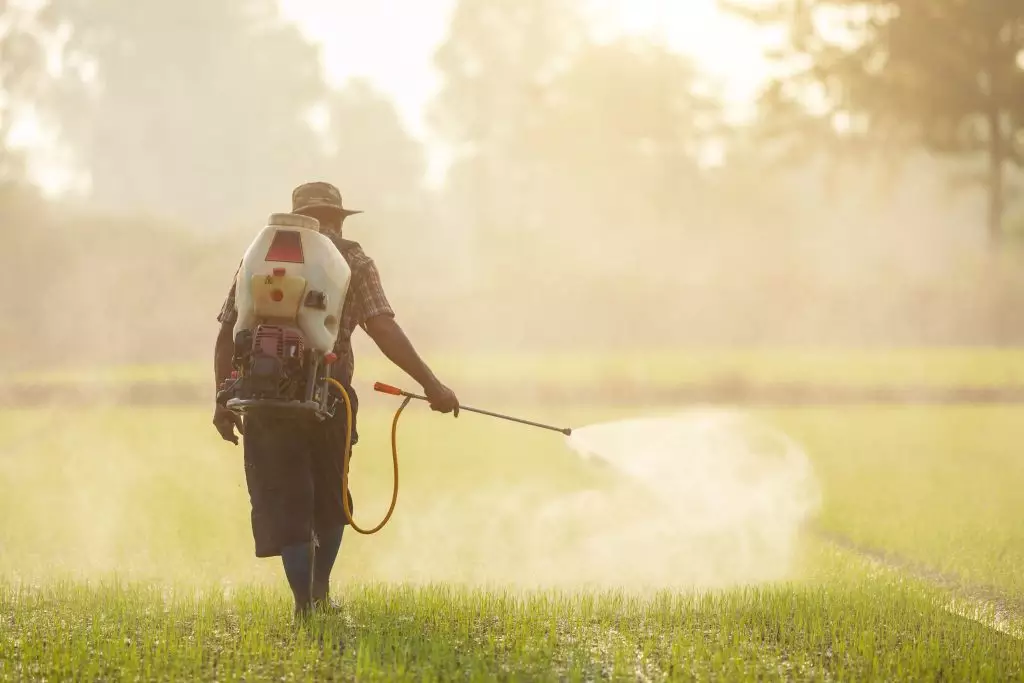

Agrochemicals, also known as agricultural chemicals, are chemical substances used in farming to enhance plant growth, control pests, manage weeds, and improve soil fertility. These substances can be broadly classified into three main categories: fertilizers, pesticides, and plant growth regulators.
Types and Benefits of Agrochemicals
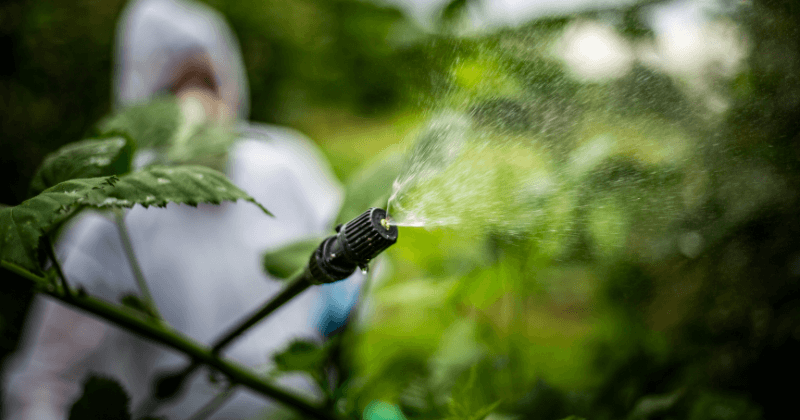

- Fertilizers: Fertilizers provide essential nutrients to crops, promoting healthy growth and higher yields. They can be classified as organic or inorganic, with organic fertilizers derived from natural sources and inorganic fertilizers typically synthesized chemically. The controlled application of fertilizers ensures optimized nutrient uptake and minimizes environmental impact.
- Pesticides: Pesticides are substances used to control pests, including insects, weeds, fungi, and diseases that can harm crops. They can be categorized as insecticides, herbicides, fungicides, and bactericides. Responsible pesticide use involves proper application techniques, adherence to safety guidelines, and consideration of environmental impacts.
- Plant Growth Regulators: Plant growth regulators (PGRs) are chemicals that influence plant growth and development. They can stimulate or inhibit certain physiological processes, such as seed germination, flowering, and fruit ripening. PGRs offer benefits like increased crop uniformity, enhanced fruit quality, and improved post-harvest shelf life.
Responsible Agrochemical Usage (agrochemical)

- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): IPM involves a holistic approach to pest control, combining various strategies such as biological control, crop rotation, and targeted pesticide application. This approach minimizes pesticide use, preserves natural predators, and promotes long-term sustainability.
- Good Agricultural Practices (GAPs): Adhering to GAPs ensures responsible agrochemical use. This includes following recommended dosage and application methods, proper storage and disposal of agrochemicals, and complying with safety regulations to protect human health and the environment.
Balancing Productivity and Sustainability (agrochemical)

Agrochemicals, when used responsibly, can help strike a balance between agricultural productivity and environmental sustainability. By optimizing crop yield and minimizing losses due to pests and diseases, agrochemicals contribute to food security and economic stability. However, it is crucial to adopt sustainable farming practices, reduce chemical inputs where possible, and explore alternatives to mitigate any potential negative impacts.
Conclusion
Agrochemicals have revolutionized modern agriculture by increasing crop yields and ensuring food security. When used responsibly, these chemicals play a crucial role in sustainable farming practices. Farmers and stakeholders must prioritize responsible agrochemical usage, following best practices and embracing integrated approaches that safeguard the environment, protect human health, and support long-term agricultural productivity.


Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.